Generation and Management of Waste
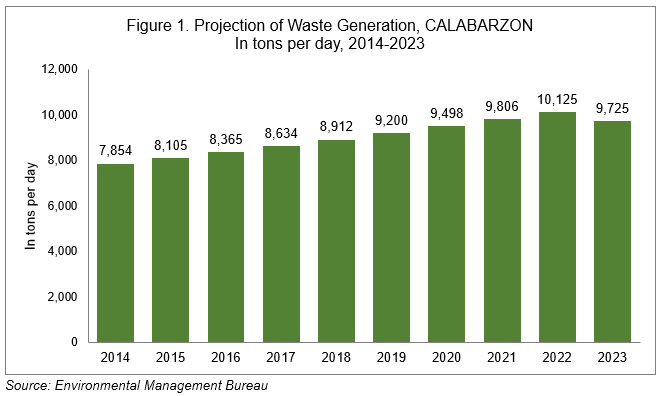
From 2014 to 2022, there was a consistent increase in the volume of projected waste generation, rising from 7,854 tons per day in 2014 to 10,125 tons per day in 2022. However, in 2023, the trend recorded a reversal with a decrease to 9,725 tons per day, marking a 4.0 percent reduction from the previous year. The projection of waste generation is derived by waste generation rate per capita multiplied by the population.
Hazardous waste is a special group of waste that, due to its toxic or other hazardous character, requires special management and is controlled by law in many countries (UN FDES, 2013). In the Philippines, the management of hazardous wastes is governed by the Republic Act No. 6969, known as the “Toxic Substances and Hazardous and Nuclear Wastes Control Act of 1990”.
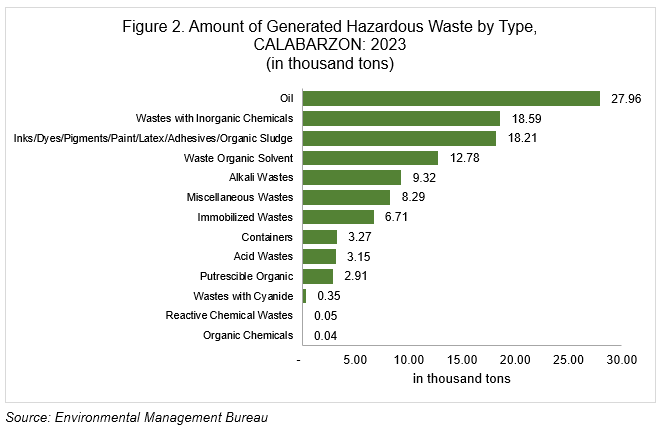
In 2023, the country generated a total of 238.26 thousand tons of hazardous waste. CALABARZON generated a total of 111.61 thousand tons of hazardous waste, which accounts for approximately 46.8 percent of the total hazardous waste in the Philippines.
Among the 13 types of generated hazardous waste, oil was the largest comprising 25.1 percent share or 27.96 thousand tons. It was followed by waste with inorganic chemicals such as selenium, arsenic, barium, cadmium, mercury, fluoride, and their compounds, which made up 16.7 percent or about 18.59 thousand tons and Inks/Dyes/Pigments/Paint/Latex/Adhesives/ Organic Sludge, which constituted 16.3 percent or 18.21 thousand tons. Meanwhile, organic chemicals like wastes with specific halogenated and non-halogenated toxic organic chemicals, ozone depleting substances and polychlorinated biphenyl wastes had the lowest amount of waste generated in the region with 0.04 thousand tons.
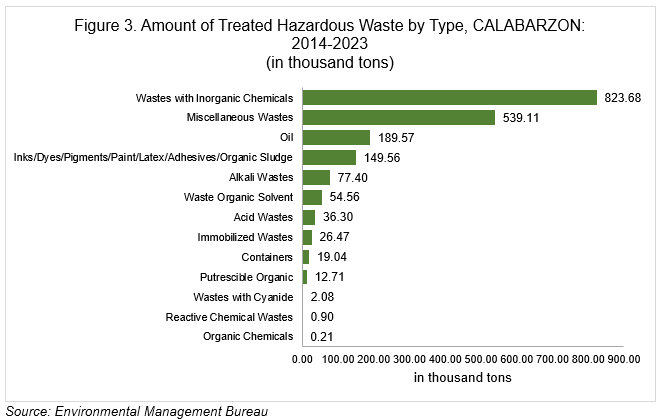
From 2014 to 2023, about 823.68 thousand tons of wastes containing inorganic chemicals were treated, making it the largest category among the 13 types of generated hazardous waste in the region. Miscellaneous wastes, such as pathological or infectious wastes, pharmaceuticals and drugs, pesticides, and waste electrical and electronic equipment, followed comprising about 539.11 thousand tons, and oil at 189.57 thousand tons.
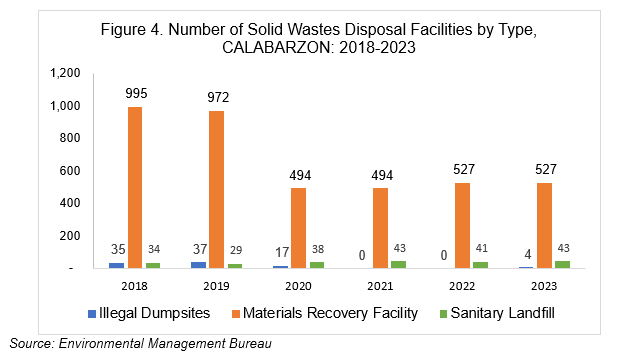
There are various solid wastes disposal facilities in CALABARZON including illegal dumpsites, materials recovery facilities and sanitary landfills. In 2023, CALABARZON recorded 527 material recovery facilities, a decrease of 47.0 percent compared to 995 facilities operating in 2018. Likewise, the number of illegal dumpsites in the region decreased from 34 in 2018 to only 4 recorded in 2023. Meanwhile, the number of sanitary landfills in the region increased to 43.
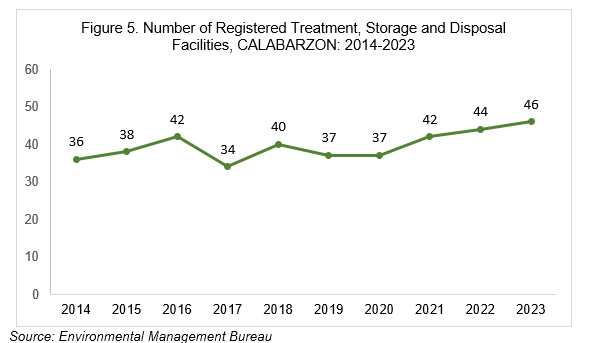
Over the past decade, the number of registered treatment, storage and disposal (TSD) facilities in the region has shown an increasing trend. As of 2023, 46 TSD facilities were registered in the region. TSD facilities are facilities where hazardous wastes are transported, stored, treated, recycled, or disposed of.
(SGD.)
CHARITO C. ARMONIA
Regional Director
COB/LOM
